While shopping for ethernet cables, you may have noticed the 24 AWG wire embedded in the cable jacket. You may have wondered what the term ethernet wire gauge means and how the gauge of wire affects the performance and type of cable making.
Table of Contents
- How Does AWG Affect Performance?
- 24 Gauge Wire Understanding
- 24 AWG Wire Patch Cables Vs. 23 AWG Wire Patch Cables
- 24 AWG Wire Cable Vs. 28 AWG Patch Cable
- Conclusion:
How Does AWG Affect Performance?
Surprisingly, cable sizes and AWG sizes share an inverted relationship. That’s because the thicker the cable, the lower the AWG size. For example, a 22 AWG wire is more comprehensive than a 24 AWG wire.
When you hear the term AWG cable, it most likely refers to wires used in the cable. The AWG size of a line is determined by the diameter and thickness of the wires used to make the cable. Therefore, cables with a larger AWG size have thinner wires than those with a smaller AWG size.
Due to such characteristics, most AWG cables are made with stranded wires. The stranded copper hook-up wire makes the cables flexible and suitable for short runs.
Cables with smaller AWG sizes are often solid cables made of thick wires. Such cables are made of more copper wire, making them perfect for covering long distances. Most likely, cables with a smaller gauge are made of jacket types like plenum, outdoor, and riser. The cables are retardant materials suitable for application in every industry and location.
24 Gauge Wire Understanding
Often, 24 AWG wires are used to cover shorter runs. Their slim size makes them able to fit through tight spaces and occupy very little space. They also offer thin wall insulation, making them a preferred choice in cases where space is an issue. For this reason, 24 AWG wires are primarily used in the internal wiring of electronic devices and appliances.
Because of their thickness, 24 gauge wires are a common choice for telecom rooms and data centers. However, depending on the wire length and maximum wire temperature safety guidelines, the amount of current carried in the wires varies. For example, the current transporting capacity of the copper wires is a maximum of 7A at a surrounding temperature of 300 degrees Celsius.
24 AWG Wire Patch Cables Vs. 23 AWG Wire Patch Cables
Patch cables are mainly made of four balanced twisted pairs of wires. And standard ethernet cable is typically 23 or 24 AWG from most manufacturers. However, 24 AWG wires are often the preferred choice for various reasons.

Patch cable
The Hose Pipe Explanation
To better understand gauges from the ethernet perspective, it’s best first to understand the elements that go into making the cables. Not necessarily the materials and components used in making the cable but the actual product that passes through the line.
Today in the ethernet cable industry, the product passing through the cable is referred to as the current flow of electrons. The logic behind the pipes is similar to that of a regular line; the wider it is, the more the water passes through it and faster. The same principle applies to ethernet cables because, for instance, a more comprehensive line means electrons flow through it more quickly.
On the other hand, thinner cables mean electrons flow at a slower rate, resulting in heat buildup and causing some electrons to dissipate. However, you can prevent the evaporation of electrons via resistance.
Smaller Is Bigger!
To measure the thickness of a cable, you could use a wire gauge measuring tool like the one shown in the image below. A gauge is labeled from the number of sizing dies needed to obtain the correct diameter. The gauge sizes directly relate to wire diameter, with the lowest five representing the most comprehensive cable and the most significant point of the scale 36 representing the thinnest cable.
The 24 AWG cable, 0.52 mm wide, is slightly different in size from the 23 AWG cable, which is 0.57 mm wide. Therefore, the smaller the AWG size, the wider the cable, meaning more copper runs through it. You can increase electron flow and resistance in the cable by increasing its diameter.
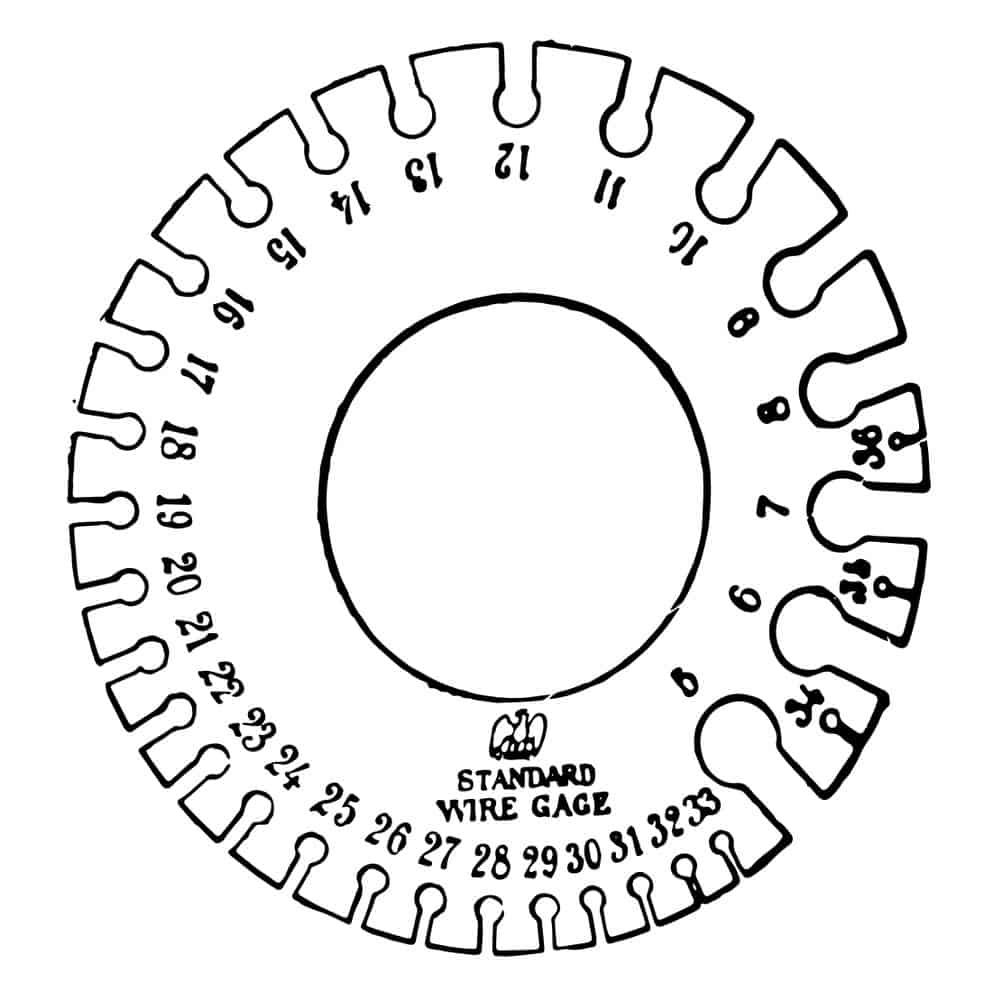
Wire gauge measurement system
Cable Performance
That said, whether the cable size affects its performance remains. The answer is no since the twisting rate is just as important as the cable’s gauge size.
However, it’s important to remember the significance of the twisting rate to the performance of category cables. A 24 AWG cable with a high twist rate will most likely do the job effectively.
24 AWG Wire Cable Vs. 28 AWG Patch Cable
You also have versions like slim ethernet (28 AWG) and flat ethernet (32 AWG). At this time, how to choose?
The Wire Diameter Of Conductors
The wider diameter of the 24 AWG patch cables allows an active conductor that serves as an advantage when routing through machines and various equipment. A 24 AWG cable has a diameter of 0.02 inches, while a 28 AWG cable has a diameter of 0.01 inches.
Transmission Distance and Speed
The transmission speed of a cable has nothing to do with the wire gauge size; hence, the emergence of more than one type of network cable.
Generally, you’ll find cables made of copper with a wider diameter in more considerable lengths because they experience minimal signal resistance, allowing signals to travel longer distances.
Therefore, 24AWG cables are the better option for longer distances where you need a spool of wire, while the larger 28 AWG gauge cables better serve short distances.
Attenuation and Resistance
The wider a cable’s diameter, the lower the electrical resistance of the signal passed through the line.
Regarding signal resistance, 24 AWG ethernet cables are a better option than 28 AWG cables. 24 AWG cables are long-lasting and experience a lower attenuation over a distance because they contain a significant amount of the conductor.
Today, the slimmer versions of Cat 6a, Cat 6, and Cat 5e thin patch cables made from 28 AWG wire have grown significantly popular, and for a good reason. These new versions are 20% slimmer than their counterparts, enhancing their airflow in a high-density rack. They’re also easy to install in tight spaces as they occupy a small space.
28 AWG Vs. 26 AWG Vs. 24 AWG Patch Cable
The gauge of the conductor largely influences the cable size. 28 AWG cables are especially beneficial in data centers and telecom rooms because they help reduce costs, save time, save space, provide high-density layouts, and simplify cable management.
The thinner an electrical wire, the more the signal flow resistance. Therefore, network cables with a smaller gauge support longer transmission distances.
28 AWG cables are not ideal for long distances because of the increased resistance that could produce heat that could lead to electrical fires.

Wire stripping tool
Conclusion:
There you have it; all you need to know about cable AWG size to help you make a more informed decision the next time you’re shopping for ethernet cables. Feel free to contact us for any assistance you may need.
