Cable assemblies serve different purposes. Sometimes, they are even for life-saving systems. So, the cable should be strong to bear all kinds of mechanical stress and be durable in its operational environment. In addition, each cable assembly must match the original design. So, before using them, you must validate the harnesses with cable harness testing. Today, we will learn about different cable harness tests and how.
Table of Contents
- Why are Tests Required?
- When are The Tests Performed?
- What tests are Required?
- Conclusion
Why are Tests Required?
- First, products have to undergo several mechanical, environmental and electrical tests during development to ensure safety.
- In addition, manufacturers have to perform in-process or final cable testing based on the end application requirements.
- Last, the manufacturer can avoid mistakes before launching a custom cable assembly build and taking them into use.

Image: large loops of electric cables
When are The Tests Performed?
- Usually, manufacturers can either complete the tests on the cable built or at a quantity of AQL (acceptance quantity limit).
- Sometimes, manufacturers may need to perform the tests in-process to ensure the completion of a specific manufacturing step.
- Apart from this, performing cable harness post-installation testing is also a great idea.
What tests are Required?
As the cable assembly connects two devices, the electrical continuity test is the standard test. As for other tests, such as insulation resistance test, contact resistance test, etc., depending on the assembly’s use and end customer. And if you need cable assemblies in aerospace, medical, or automotive applications, you must consider another testing to ensure their validity.
Full Visual
As the name suggests, these are visual tests that need your attentive eyes to detect apparent faults. Here you need to look for the right parts and their quantity.
- Cable length
- Wire color and gauge
- Pull test on crimp
- Contamination free contacts
- Any broken strands
- Correct registration of IDC cables
Electrical Testing Requirements
Electrical tests ensure the electrical properties of the wiring harnesses. You must source the mating connectors and assemble them to the test apparatus for testing.
Electrical continuity test
- The confirms the proper connections between wires and connectors by checking if the current flows smoothly.
- It measures the circuit’s connection resistance or active resistance.
- It detects any broken wires or damaged conductors and other variety of components.
How to perform?
- First, connect the two or more testing points to a multimeter. The multimeter measures resistance and continuity.
- Now, when you switch on the multimeter, it sends a small voltage between the two test points.
- You get the overall circuit resistance. Some multimeter confirms electrical continuity through a deep audible beep.
- If there is an open circuit, you get an open-loop message on the multimeter.
- You can test all the legs of a multi-conductor cable using automatic multiconductor testers and proper fixture clamps. You need not check every conductor set; however, you must customize this automated test equipment according to the cable harness configurations.
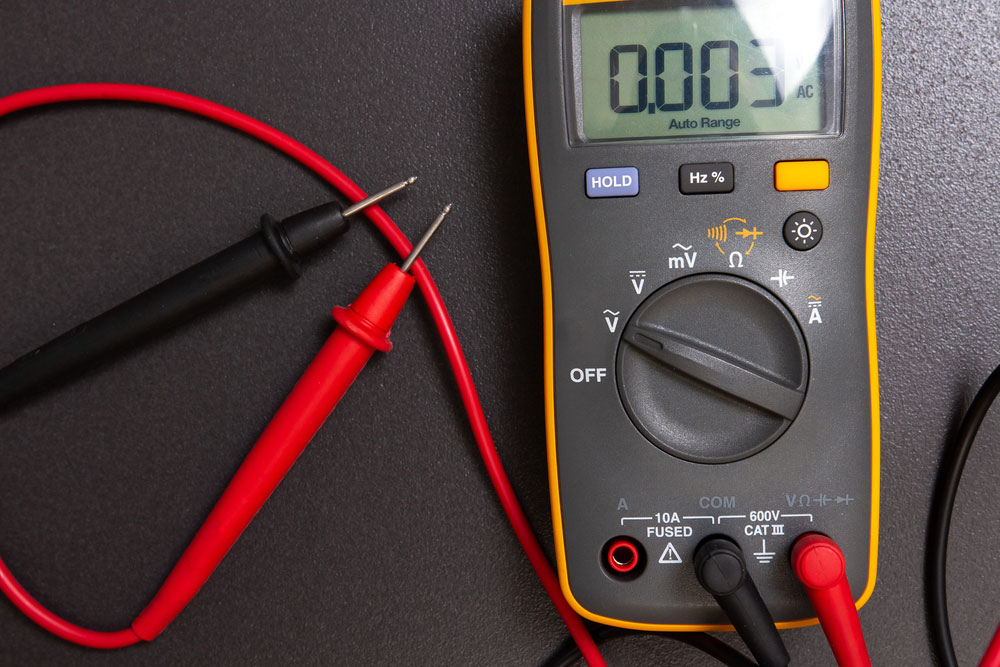
Image: multimeter: tester probe for electric measure
Hipot test/Dielectric strength test
- First, it evaluates the insulation jacket of the cable for any gaps, defects, or contamination.
- Second, it detects any current leakage or any internal short circuits.
How to perform?
- First, a high voltage of around 10 kV passes through the two conductors. This high voltage will stress the insulation jacket and the soldering connections.
- Now, if the circuit withstands that voltage for a specific period, it verifies that cable assembly is safe to use during the application’s lifespan.
- For multiconductor cable assemblies with more than 20 conductors, the Hipot test systems test all adjacent conductors. Although there is automatic testing equipment for such assemblies, they are costly.
Milliohm test
- It ensures that the quality of the electrical connection is within acceptable values.
- It mainly measures the resistance between the cable and the ground. This resistance is meager, and the multimeter does not have resistance measurement capability for such low values; thus, you need a milliohm meter.
How to perform?
- Firstly, take a milliohm and start testing with the 4-wire resistance measurements method.
- Secondly, apply some current to a portion of the cable assembly.
- Now, measure the voltage at two terminals.
- Finally, measure the current sensing at the other two terminals.
- The cable is suitable to go if the test shows 2.5 milliohms of resistance between two ground points. And if the resistance is more than permissible resistance limits, there is a need for cable evaluation.

Image: technician using digital cable analyzer
Cable Harness Testing: Mechanical testing requirements
Mechanical testing tests the strength of a cable assembly. For this, the cable assembly goes through several stress tests.
Pull Test
- It checks the strength of the cable, connectors, and crimp joints. You can perform a pull test in different ways:
Pull and break: A destructive test where you apply the force on the cable until it fails.
Pull, hold and break: Again, a destructive test where you use a force, have it for a specific rate. Again, you increase the pressure until the connectors or wire break.
Pull and hold: A non-destructive test applies a force at a specific rate and has it for a particular period.
Pull and release: Another non-destructive test where you pull the cable at a specific rate and remove the force.
How to perform?
- First, you apply a specific pulling force to the cable assembly based on the cable type and the connectors. You can use the force through an automated test station or manual weights.
- As you do this, connect a motorized pull tester to measure the amount of force. Based on the application requirements, test results are announced.
Cable Harness Testing: Flex/Bend test
- It determines the cable’s capability to withstand bending, twisting, or flexing during its applications.
How to perform?
- Firstly, attach a bend/flex machine to one end of the cable.
- Secondly, attach a weight or tie the cable to a pretzel shape to bend it to a 90-degree angle.
- Sometimes, to perform a rolling end test, you need to attach the second end of the cable to the swing arm mechanism. It constantly flexes the cable while swinging at 180 degrees.
- To perform the test, you must know the minimum bend radius and the number of cycles.
Environmental testing requirements
Standard environmental tests are vibration, humidity, waterproofness, thermal shock, temperature storage, fungus exposure, chemical and fluids exposure, and salt spray.
Cable Harness Testing: IP66/IP67 Water Ingress Protection codes
IEC codes are essential to give the protection rating to a cable used in different environments and applications. And the protection ratings mainly fall under International Protection (IP) code standards. Here IP also refers to the “Ingress Protection.”
In every IP code, you will find two numbers. The first number indicates the protection rate from dust, dirt, or other solid matter. And the second number specifies the rate of protection against liquid substances, especially water.
And the two most common ratings in this category are:
IP66 Rating: This rating indicates that the cable assembly offers total protection from dust and dirt (indicated by the first” 6″). Here, the second “6” shows protection against water ingression from high-power water jets at any angle.
IP67 Rating: The first “6” indicates complete dust and dirt protection in this rating. On the other hand, the number “7” specifies that the cable assembly shows moisture resistance if submerged in water to a depth of 15cm to 1m for half an hour.
Cable Harness Testing: Fungal Resilience test
Some applications use cable assemblies in warm, humid conditions where darkness and moisture persist for a long time. In such environments, cable assemblies show fungal growth, damaging insulation jackets, conductors, or connectors, corrosion, aging, and other issues. In such cases, the cable assembly must pass a United States military standard test as per MIL-STD-810 to ensure that a cable is resistant to such fungal growth,
Spray a material coupon with fungus spores to test its effectiveness in this test. Put that coupon in a warm, humid chamber that can promote fungal growth. Monitor the coupons for any change after a few days.
Conclusion
Performing a wiring harness test requires time and sometimes a particular wire harness tester. Both can lead to a higher overall cost of the cable harnesses. Further, some tests can also damage the cable assembly. So, it is advisable to review the test details in advance. And at Cloom, we perform inspections with our advanced testers so that you can have high-quality cable assemblies.
