Most manufacturers design the cables specifically for the outside while considering all the environmental factors. So you can find cables with varying levels of roughness in the market. This guide will give you 4 useful suggestions for selecting the correct cable jacket type. But before that, you are supposed to know the basics of cable jacketing.
Table of Contents
- What is a Cable Jacket?
- What Cable Jacket Characteristics Do You Need?
- Types of Cable Jackets
- Tips for Selecting Cable Jacket Material
- Physical properties of standard insulation and jacket material
- Conclusion
What is a Cable Jacket?
The cable jacket is the first line of defense against water, damage, fire, and chemicals. It keeps the conductors and shielding inside the cable from wear and tear. Moreover, it also keeps the line from being harmed when installing and setting it up.
However, cable jackets do not mean that you need to replace the reinforced armor on the inside of the cable, but they can offer some protection. Additionally, cable jackets also protect against UV radiation and ozone.
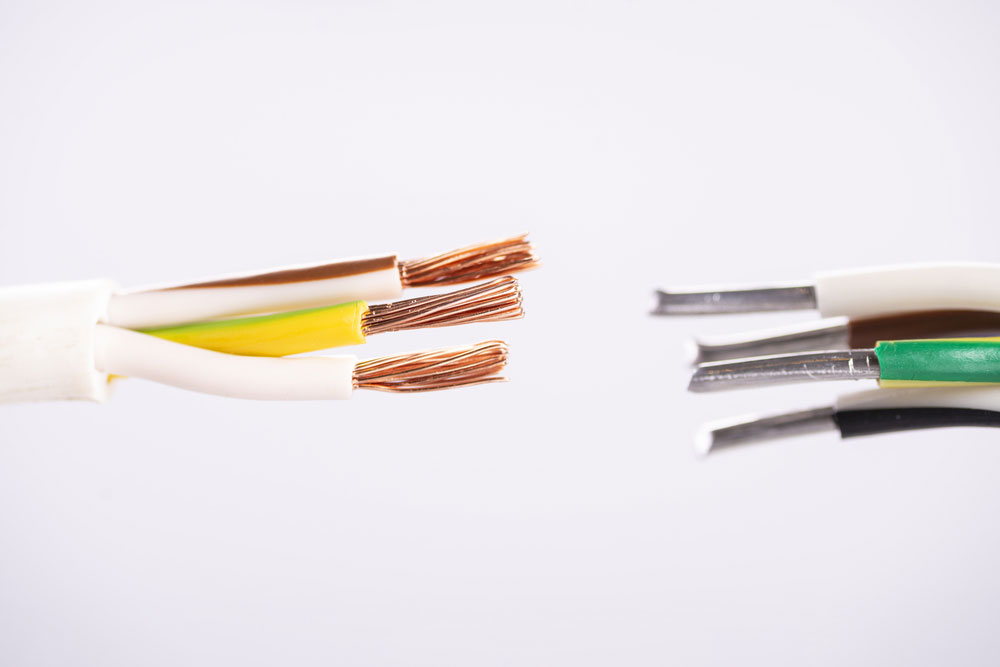

Caption: Cable jacketing, White
What Cable Jacket Characteristics Do You Need?
Some essential characteristics of cable jacketing that can benefit you are
- Flexibility, for ease of use and a longer flex life
- Color for identifying between different cable types (for safety, e.g., red for hot wire, green for neutral, etc.)
- Surface Texture, for ease in installation and handling
- Elastic memory, for maintaining its original shape, especially in coil cord
- Chemical Resistance, for durability in a chemically exposed environment
- Low-Temperature Flexibility, for use in polar regions where there is a harsh cold environment, such as arctic
- Extreme Temperatures Survivability, for good ampacity ratings, ambient, and peak operating temperature.
- Flame Resistance, for safety in case of fire and flame, spread
- Approvals/Compliance for checking whether the cable is suitable for an application or not.
Types of Cable Jackets
There are two cable jacket types.
Thermoplastic
Thermoplastic includes materials capable of fusing or softening when you heat it. As soon as it cools down, it hardens again. That means you can reuse these plastics many times. Thus, when you want to cover the conductor, you can place it over the wire and heat it to extrude over the conductor.
Some prominent features are
- Easy to manufacture
- Normally budget-friendly
- No curing needed
- You can extrude it even on thin walls
- Will melt as you expose it to heat
Common thermoplastics are Polyvinyl Chloride PVC cables, Thermoplastic polyurethane TPU, Thermoplastic Elastomer TPE, etc.
Thermoset
On the other side, thermoset refers to the material group that does not soften upon heating. Thus, you cannot melt it down or reuse it once it has been cured.
Some prominent features are
- Thermoset materials are not easy to manufacture
- Can easily maintain their shape when overloaded
- Hardens as you expose it to overheating
- Has good low-temperature performance
- Has higher temperature endurance
- Expensive than thermoplastics
- When extruded, it requires extruding
- You cannot extrude the thermoset smaller than 22 AWG. In smaller sizes, use irradiated products for extrusion.
- However, they offer higher durability and longer life cycles.
Few thermoset materials are Ethylene Propylene Rubber EPR, Silicone, Cross-linked Polyethylene XLP, etc.

Caption: Colorful cable jackets
Tips for Selecting Cable Jacket Material
Here are a few questions you need to consider before choosing a jacketing material
What is the environment and type of application in which you will use it?
The application area is the critical factor in selecting the material for the cable components. The specifications may change depending on the environment, whether jacketing or conductor. For instance, you need biocompatible and free of germs jacketing material in the hospitals.
Additionally, you will choose the material based on temperature range, abrasion resistance, flexing, frequency of exposure, etc.
Does the cable require approvals?
In some cases, you need specific standards and ratings for the cable. Thus, if the cabling needs CSA marking or UL approval, you need to look for these requirements while searching the market.
Will, you over-mold a connector to the jacket?
It is critical to identify both the over-mold material and the jacket’s material to make sure they will stick to each other. Aside from the material, the shape is also a crucial factor. Thus, if the cable has an over-mold, you have to shape it around for a good grip. Moreover, a pressure jacket is better than a tubed jacket for most applications.
Does the assembly require stripping the jacket? If so, what will be the length?
When deciding on the correct jacket type, you should think about any processes that will follow, like stripping and the tools that you will use. Some materials are better to handle than others. For instance, polyurethane is harder to cut and peel than a PVC. Moreover, if you keep the strip length longer at the cable end, a jacket with tubes will make it easier and faster to strip.
Physical properties of standard insulation and jacket material
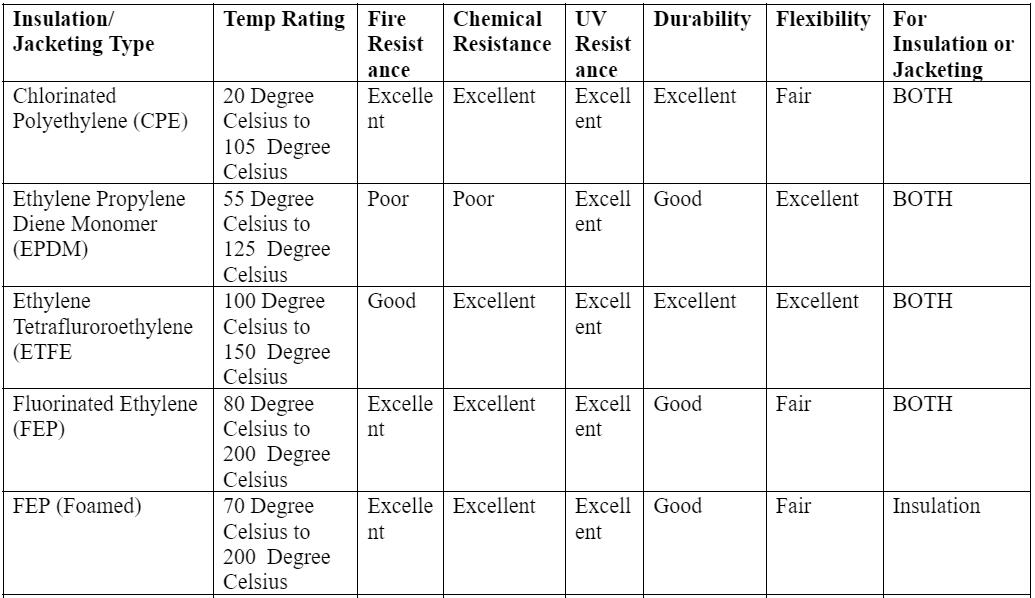
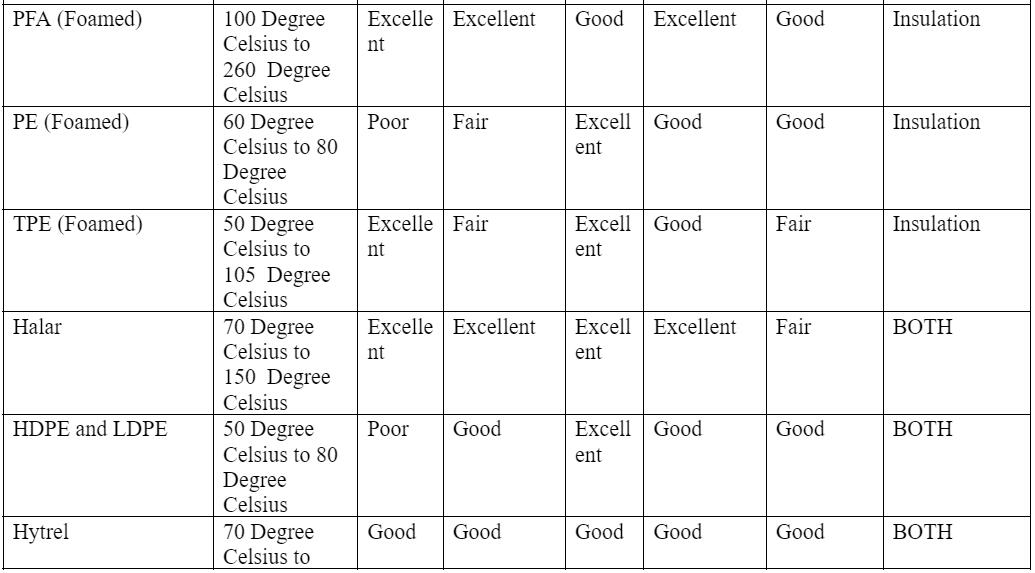
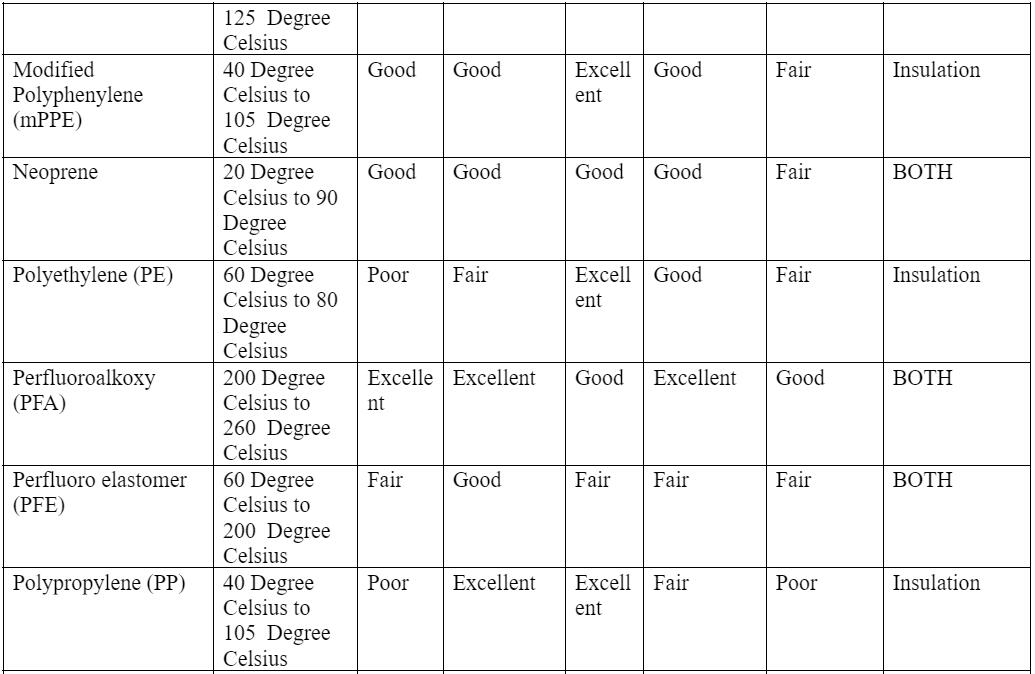
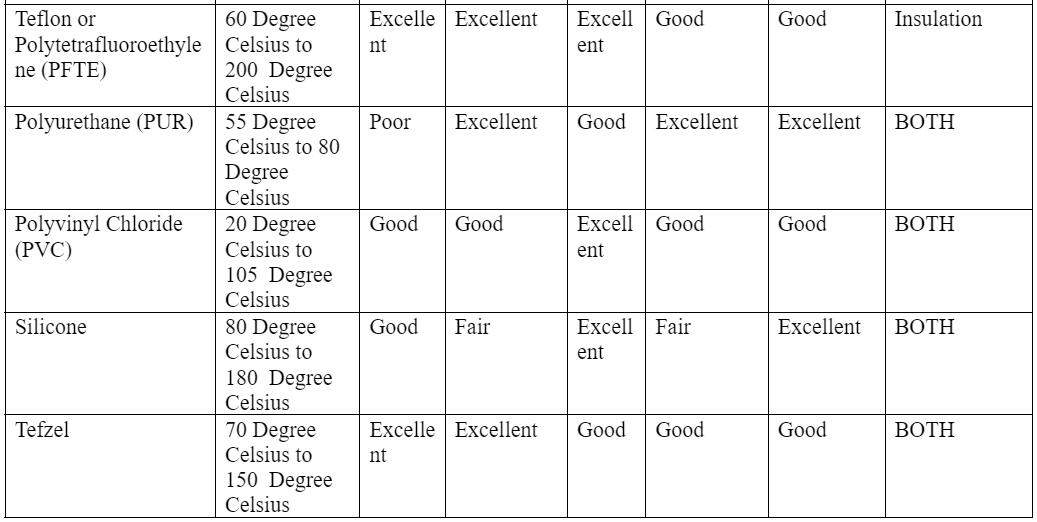
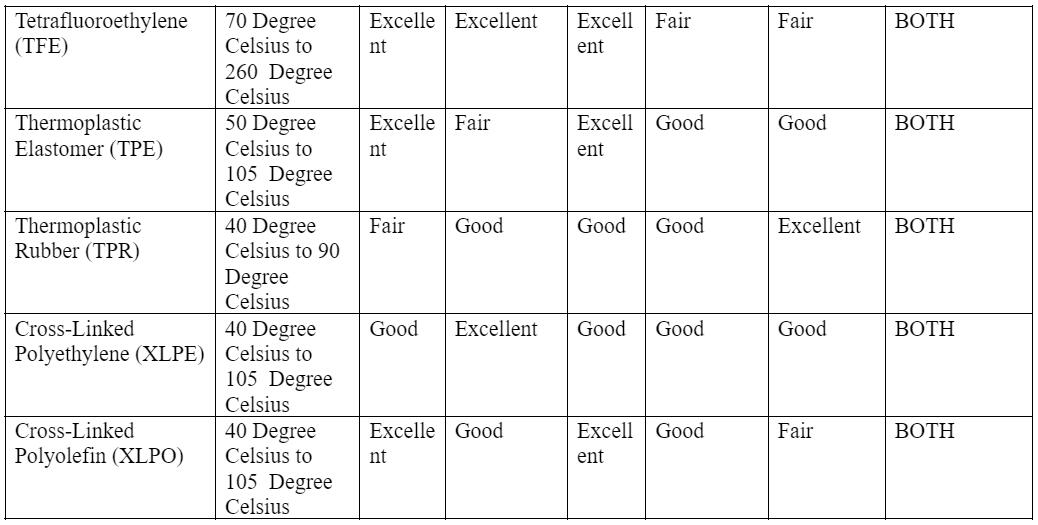
Caption: Solid and Stranded Wire Layering
Conclusion
Cable jacketing is vital for protecting the inside of the cable from abrasions, moisture, and chemicals. Depending on the preferences and application, it can be either thermoplastic or thermosets. Moreover, it would help consider the over-molding, jacket stripping, and certifications while selecting the jacket material. Here at Cloom, we offer wiring harnesses and cable assemblies with a wide range of jacketing materials, so your connection is made with attention to detail.
