Ethernet is a collection of wired computer networking technologies. They serve in Local, Metropolitan, and Wide Area Networks. Also, they are compatible with personal computers(PCs), making them ideal for all users. Ever been curious about how to choose one suited for you? This guide will give you a deeper understanding of the ethernet cables cat, which is important in your choice.
Table of Contents
- Ethernet Cables cat: What are Ethernet Cables?
- Ethernet Cables cat: What does Cat mean?
- Ethernet Cable Categories
- How To Choose the Ethernet Cable
- Conclusion
Ethernet Cables cat: What are Ethernet Cables?
Ethernet cables transfer broadband signals between devices on LAN systems. They use twisted pairs of conductor wires to reduce electrical interference. The devices include routers, modems, personal computers, and wired internet cables.
Ethernet cables improve your internet speed and stability. They are available in different varieties.
Ethernet Cables cat: What does Cat mean?
When searching for cables that best fit your internet services, you’ll realize the cables are available in different groups. That is, by “cat” numbers.
“cat” is a short form for the category. Next to the “cat,” you will see figures representing the cable’s specifications. You measure frequency in megahertz(MHz).
Similarly, the more advanced the cables are, the better the performance. Also, newer cables hold up more bandwidth, which means there will be an improvement in internet speed and connections.
Ethernet Cable Categories
There are plenty of ethernet categories in the market. The most common types are Cat5, Cat6, Cat7, and Cat8. Depending on your devices, you can choose the proper category.
Cat1
Cat1 cables are also known as voice-grade copper. This type of cable was the most common in premises wiring for analog communications. They were forms of wiring for telephone communications in offices and homes.
The highest transmission for this category is 1MHz. Currently, it’s not deemed enough for data transmission.
Cat2
This category was responsible for telephone and data communications. The maximum frequency for this category is 4MHz. Also, it has a maximum bandwidth of 4 Mbits/s and four pairs of wires.
Cat3
Manufacturers introduced this category in the 1990s. It is an unshielded twisted pair used in digital voice communications. These cables were the first to support a 10Base-T network.
These cables are still available in old buildings, and users use them for alarm system installation. However, they only support up to 10 Mbps which is less reliable in the current networking.
Cat4
Cat4 cable is a cable with eight pairs of copper wires. Manufacturers organized the copper wires in four unshielded twisted pairs. These categories are currently found in old buildings.
The current ANSI/TIA-568 data cabling standard can’t recognize them.
Cat5
Cat5 cables were introduced in 1995 and provide up to 100MHz performance. They are the most common versions that most people use because of their cost-effective price and faster speed.
.
They are best for ethernet-shielded twisted wire pairs between 100Base-T and 2.5GBase-T. However, it mostly runs at 1000Base-T. It’s also used for video and telephone and can distribute data signals up to a distance of 100 meters.
On the other hand, manufacturers use cat5e cables to enhance cat5 cables to a speed of 1.5Gbps. In short, cat5e is an enhanced Cat5 cable. To identify the difference between the two, Cat5e will have 5e instead of 5 on the cable sheath.
Cat5e improves the cat5 specifications by alleviating the number of crosstalks. Both meet the same bandwidth capabilities of 100MHz.
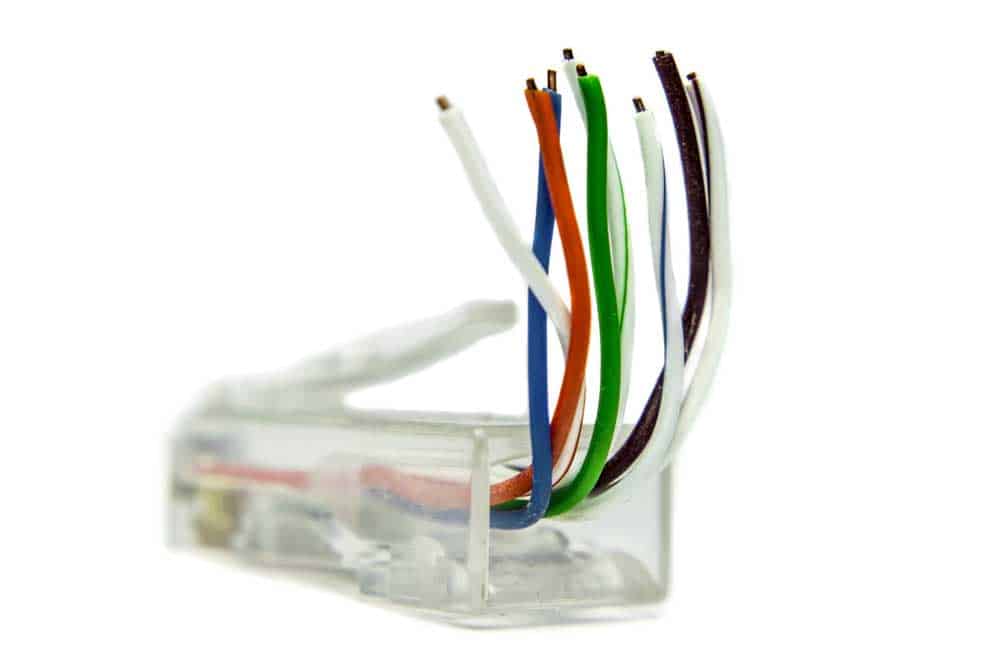
cat5 connector
Cat6
Cat6 ethernet cable is a twisted pair cable that has some comparison with the Cat5 ethernet cable. This cable has greater bandwidth and can convey data of up to 1Gbps over a distance of 100m. The same way Cat5 cables work.
But, these cables also allow data transmission of up to 10Gbps over a shorter distance due to higher bandwidth frequencies and enhanced shielding. They also ran a frequency of up to 250MHz.
Cat6 cable is designed with foil shielding to lessen electromagnetic disruptions.
In addition, it has a spline among the four pairs to reduce crosstalk and provide a higher signal-to-noise ratio.
The four-pair cable also increases airflow in congested equipment. In 2009, manufacturers introduced Cat6a cables to enhance Cat6 specifications.
Cat6a ethernet cable supports a frequency of up to 500 MHz bandwidth, and each pair has metal shielding to reduce further disruptions.
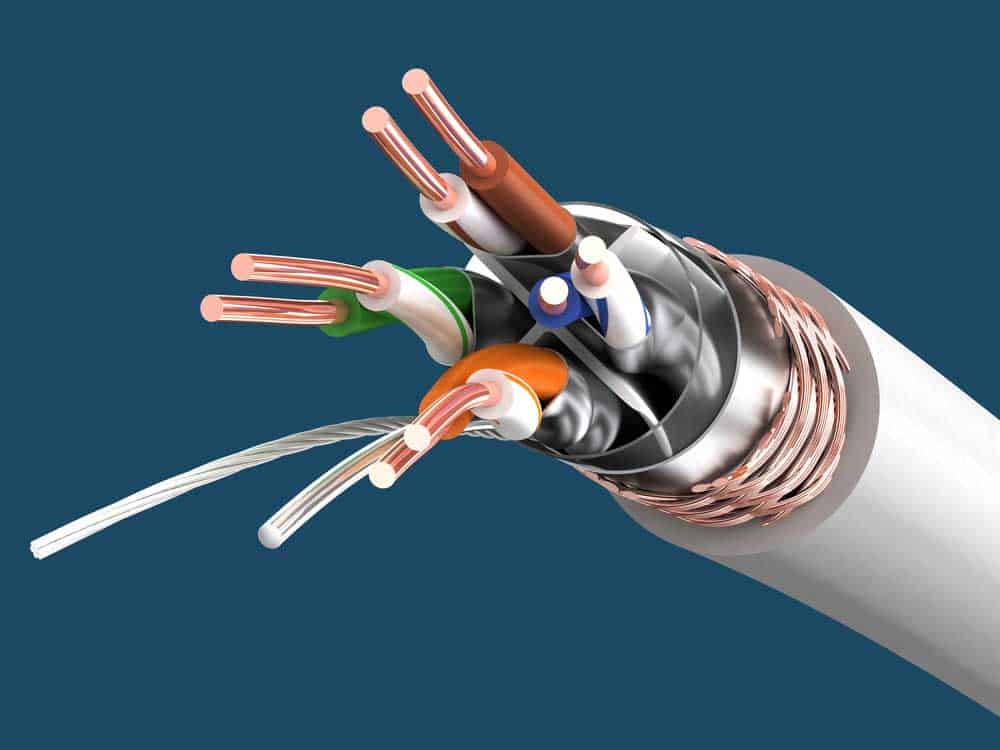
Cat6a twisted pair
Cat7
Cat7 ethernet cables support higher frequencies than the previous generations of cabling. That is why industries that require high data transmission and performance use them.
These cables have similar specifications to Cat6a cables, except that they are shielded and need a GG45 connection. Cat7a ethernet cables are an improved version of Cat7 cables. Their speed is fast and can transfer up to 100 Gbps data at a distance of 15m.
Due to their lack of endorsement by IEEE or TIA/EIA as cable standards, these categories have been relatively small installations.
Cat8
Cat8 ethernet cables are high-category cables that support a maximum frequency of 2000MHz over 30 meters. With a maximum of 30 meters, these cables can support transmissions to PoE devices like security cameras and wireless access points when not close to AC power.
They are the newest copper ethernet cables and have a data rate of up to 40 Gbps. Due to their high frequency, their conductors have a foil shield to eliminate crosstalk and enhance data transmission speeds.
With the shielded conductors, these faster cables result in a heavier gauge cable that you can only fix in areas with ample and not tight spaces. Cat8 cables use RJ45 connectors, just like the previous generation.
The RJ45 connector comprises 8 pins spaced 1 mm apart. The wire’s function is to provide a reliable connection.
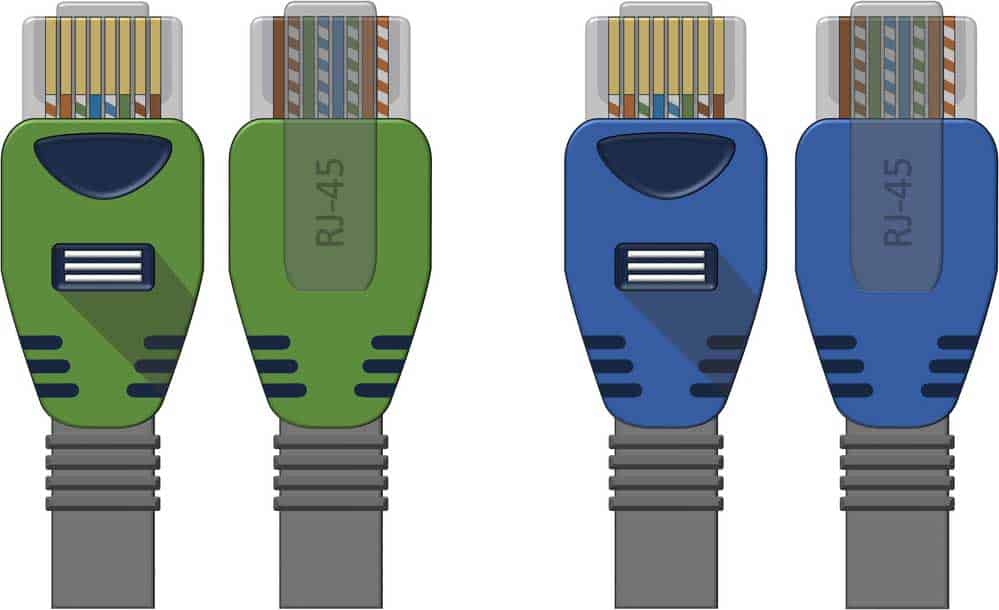
RJ45 connector network cable
How To Choose the Ethernet Cable
Choosing internet cables that best suit your needs can be excruciating. Below are some of the factors you can consider when selecting your ethernet cable cat:
Ethernet Cables cat: Tracking your internet speeds

internet speed test
Selecting a cable within your range is what you’ll need.
First, start by running your home internet speed connection. You can connect your PC to your modem and run a speed test.
Next, check on the bandwidth frequency. If you are using a lower connection, say 20 megabits, you can get Cat5 or anything above Cat5 cable.
Be keen to select a cable depending on your browsing intensity. If you are heavy on internet use, an enhanced quality cable would be ideal for your download speeds. Choosing a better cable will make a huge difference and provide high-speed internet.
Ethernet Cables cat: Shielding
When choosing an ethernet cable cat, always look out for shielding. Shielding protects the cable’s conductors from electromagnetic interference. Fluorescent lighting, power lines, and large machines may cause electromagnetic interference.
Shielding also prevents parallel conductors in the cable from interacting. Looking at the conductor gauge may be a good idea, but you are good to go once shielding is in place. Manufacturers use the American wire gauge standard sizes to refer to the diameter of the conductor gauge.
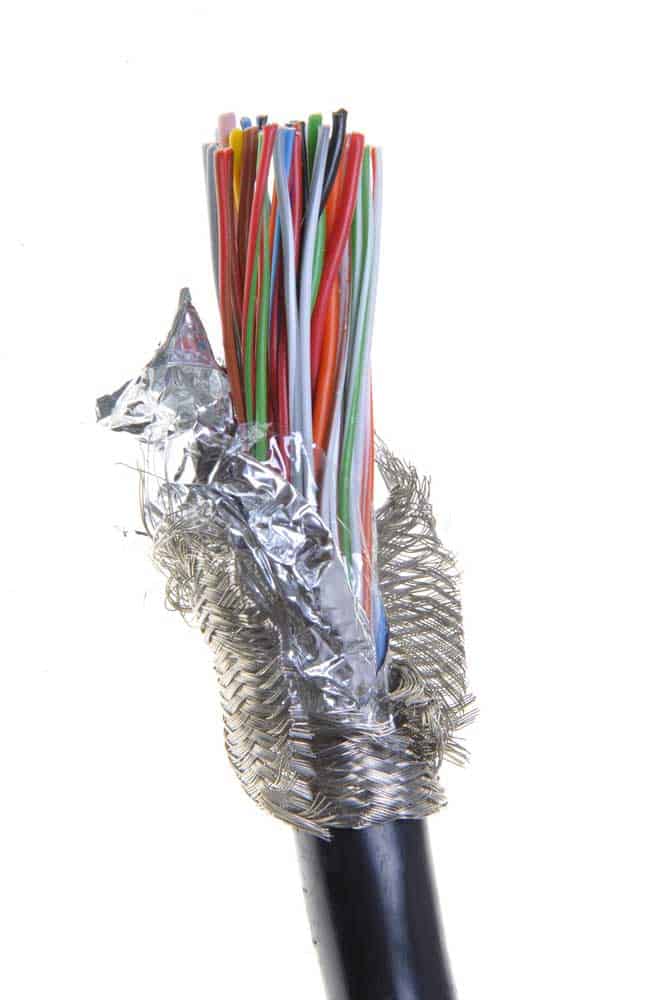

cable with shielding
Ethernet Cables cat: Cable Length
Before getting a cable, consider that cables don’t run straight. Therefore, you’ll need an extra length for twists and turns. The maximum length for cables is 90 meters.
Installation Location
Cable jackets are best for fire safety. The installation for your cable should be near an electrical outlet and away from obstructions. Therefore, you can use rise-rated (CMR cables) or plenum-rated (CMP cables) if you plan on running the cables on walls or floors.
Conclusion
Ethernet cables are available in different varieties. When choosing one, all you need is an accurate connection inform
