About All Ethernet cable types, Ethernet cable is a single name with a broad category of wires under its umbrella. Hence, these vary from Cat variations, shielding differences, pinout arrangement, etc.
In this article, we will look into various Ethernet cables that you can find in the market.
Table of Contents
- What Are Ethernet Cables?
- How Do Ethernet Cables Work?
- Ethernet Cable Types Based on Cat
- Ethernet Cable Types Based on Pinout
- Ethernet Cable Types Based on Shielding
- Ethernet Cable Types Based on Connectors
- Ethernet Cable Types Based on Jacketing
- Ethernet Cable Types Based on different designs
- Choosing the Right Ethernet Cable Type
- Conclusion
What Are Ethernet Cables?
Ethernet cables allow different network devices to connect and work with each other while creating a local network. Moreover, it enables the devices to share data and other files at higher speeds efficiently.
Although the WIFI signals have let cellphones and laptops access the internet without any cable, it couldn’t kill the popularity of Ethernet. It is since every component behind the WIFI uses these cables to propagate the signals.

Caption: Network Cable
How Do Ethernet Cables Work?
Ethernet cables work by connecting to the ports of each device. Network engineers mostly use these wires to connect WIFI routers and modems to telephone or internet lines.
You can also use the cable for linking other hardware devices like TVs and computers to make a network. Usually, engineers use twisted pair cables in a LAN for better signal propagation.
Ethernet Cable Types Based on Cat
- Cat1 was designed for basic voice communication. It has two insulated copper strands that twist around each other.
- Cat2 can send voice and data signals from one place to another. Also, it can transmit data of 4 Mbps.
- Cat3 consists of four twisted pair cables and can send data up to 10Mbps.
- Cat4 is the same as Cat3, with 16 Mbps data transmission capability.
- Cat5 can transmit data over 100 Mbps and is still used by network engineers. Additionally, its other variation, Cat5e, can send over 1GB of data without any problem.
- Cat6 can offer high data transmission with greater bandwidth, making it competitive with Cat5e. It is also backward compatible with Cat 5 and 5e. Moreover, its latest variation, Cat6a, can work over the 500MHz bandwidth.
- Cat7 differs in connectors and is different from a standard the engineers recommend. It can offer a good speed of up to 40Gbps, but the propriety differences make it lose the support of IEEE and EIA.
- Cat8 work best for switch-to-switch application in many networks. However, there are heavier in gauge and cannot be installed in closed spaces.
Ethernet Cable Types Based on Pinout
Although the quality of wiring may vary due to differences in manufacturers, the basic connection type remains the same. The following tables show each pin and its function in the data transmission.
| Pin | Wire Color | Signal | Signal Description |
| 1 | White/Green | TX1+ | Transmit + |
| 2 | Green | TX1- | Transmit – |
| 3 | White/Orange | RX+ | Receive + |
| 4 | Blue | TX2+ | Bi-Directional Transmit + |
| 5 | White/Blue | TX2- | Bi-Directional Transmit – |
| 6 | Orange | RX- | Receive – |
| 7 | White/Brown | TX3+ | Bi-Directional Transmit + |
| 8 | Brown | TX3- | Bi-Directional Transmit – |
Caption: T568A standard color code
| Pin | Wire Color | Signal | Signal Description |
| 1 | White/orange | TX1+ | Transmit + |
| 2 | Orange | TX1- | Transmit – |
| 3 | White/Green | RX+ | Receive + |
| 4 | Blue | TX2+ | Bi-Directional Transmit + |
| 5 | White/Blue | TX2- | Bi-Directional Transmit – |
| 6 | Green | RX- | Receive – |
| 7 | White/Brown | TX3+ | Bi-Directional Transmit + |
| 8 | Brown | TX3- | Bi-Directional Transmit – |
Caption: T-568B standard color code
Here, the TX stands for Transmitted data, RX for Received data, and BI_D for Bi-directional data for A, B, C, and D pins.
And according to the standard used on two ends, we can class the cable into two types.
Straight-through Cables
Conforming to the EIA/TIA-568-A or B standards, straight-through cables have the same terminations on both ends. However, most systems use the T568-B standard to terminate patch cables. Typically, you can use a straight-through Cat5 cable in a single router-to-computer connection.
Crossover cables
However, connecting two similar devices, such as PC to PC, Switch to Switch, and Router to Router requires only a T568A termination at one end and a T568B termination at the other. Crossover cables are a common name for these kinds of patch connections.
Ethernet interfaces are now intelligent enough to differentiate between straight-through and crossover cables. Then they adjust their settings according to the cable format. Hence, you don’t need to use the crossover cables as much as you think.
Moreover, crossover cables do not have a marking on them. It means you can confuse them with the straight cables, so it’s better to mark them to avoid future mix-ups.

Caption: Ethernet Jack with pinout
Ethernet Cable Types Based on Shielding
Here are the popular types of Ethernet cables according to the shielding over them.
UTP or Unshielded Twisted Pair Cable
These cables have no shielding at all. Although they are becoming oblique, many households still use them for basic home uses where they do not need heavy cables.
STP or Shielded Twisted Pair Cable
The STP means shielding is available on the cable without going into its Specifications.
FTP or Foiled Twisted Pair Cable
F in the FTP indicates a thin foil shielding over the cable. Also, it is an inexpensive form of shielding and usually uses copper or aluminum with a polyester covering.
Outer Foil Twisted Pair (F/UTP)
Outer foil shielding means that the shield is available on the overall cable. Still, the individual wires do not have any protection.
Outer Braided Twisted Pair (S/UTP)
These cables contain a thin braiding of copper or tin over the cable but not on the individual wires.
Outer Braided Shield/Foiled Twisted Pair (S/FTP)
Here, the outer cable has a thin weave of tin or copper. At the same time, the foil protects the individual wires.

UTP
Ethernet Cable Types Based on Connectors
According to different connectors, here are the common types of Ethernet cables.
RJ45
RJ45 or Registered Jack 45 is a standard connector for Ethernet cable. Thus, you will find this connector on every internet wire, from Cat1 to Cat 6a and Cat 8. For RJ-45 pins, there are two popular arrangements of wires within the Ethernet cables
- T568A
- T568B
GG45
Giga Gate 45, or GG45, is the special connector for Cat7 due to a change in standards. It is also backward compatible with RJ45.
EtherCON RJ45
Not every situation requires RJ45 since their plastic clips may break too often. To cater to the problem, Neutrik came up with a sturdy version called the Ethercon RJ45, stronger than traditional connectors.
M12-coded connectors
These are often used in industrial applications where the cable faces extreme temperatures and vibrations. In addition, the M12 connectors are threaded. Hence, they provide additional moisture resistance and sturdiness to the connection.
Molded connectors
Sometimes, the manufacturers attach the connectors to the end of cables using the technique of over-molding. Moreover, silicon or other thermoplastics cover them to form a solid piece of cable known as a boot.
While it makes the connectors permanent on the cable, it increases the durability of the wire. Thus, these cables can easily withstand more insertion cycles without breaking down.
Snagless connectors
The boot is even more modified, so the connectors can’t get off easily from the cables. Their special application includes the situations where you need to connect and disconnect the wires frequently, such as laptop-to-router connections.
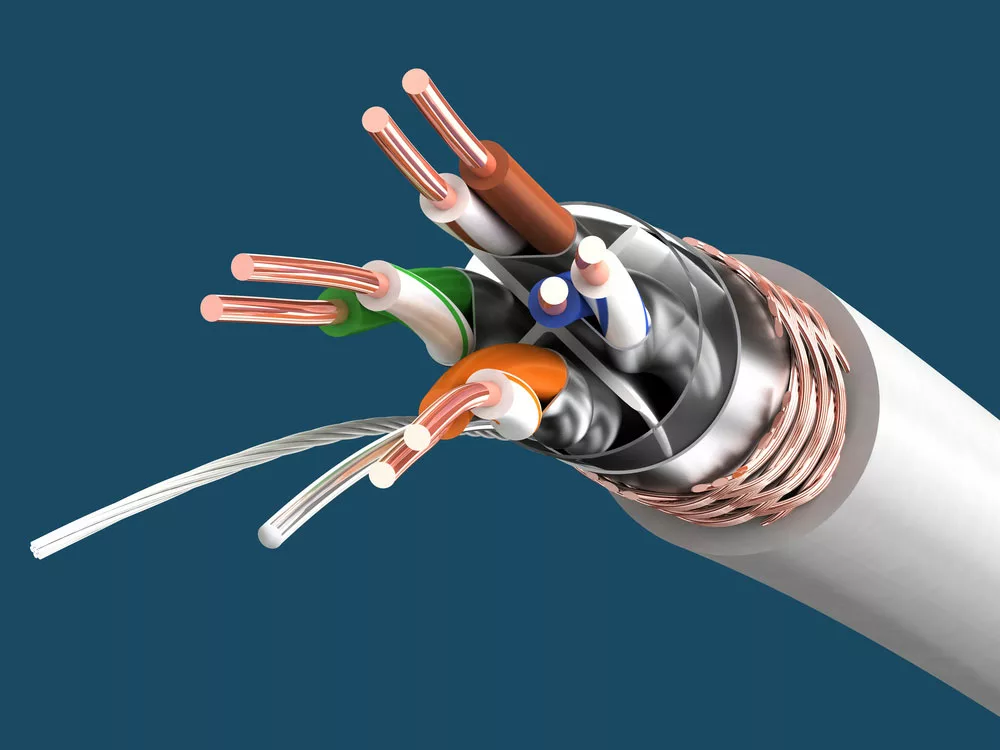
Caption: Cat 6a internal structure
Ethernet Cable Types Based on Jacketing
Jackets protect the Ethernet wires from cuts and damage. Also, they help prevent moisture, UV rays, and dust from affecting signals’ propagation. Also, different colors help you with cable management.
Jacket Ratings
Every jacket is rated according to the situation it can withstand.
| Jacket Rating | Description | Applications | Acceptable Substitute |
| CM/CMG | Communication (General) | For general purposes and basic communication in rooms. Not suitable for Plenum or Riser spaces | CMP or CMR |
| Riser (CMR) | Communication RiserRiser is a closed space between walls and floors. | For in-wall applications. | CMP |
| Plenum (CMP) | Communications Plenum A plenum is a space above the ceilings and under the floors. | For underfloor installations and other closed spaces. | |
| Outdoor (CMX) | Outdoor with Low-Density Polyethylene | For an outdoor installation that is exposed to moisture and UV light. |
Jacket Colors
Technically speaking, the color of the jacket has little significance over its performance. So, the vendors only assign the colors to differentiate between the types of Ethernet you buy.
For instance, green may indicate the crossover cable, while blue shows the cable is for routers. However, only some manufacturers follow the same rule.
Ethernet Cable Types Based on different designs
Ethernet cable styles are made with specific jobs or environments in mind, so you can tailor your cables to where you will use them. Here are some common examples:
Slim and Ultra-Slim
These Ethernet cables have a slim appearance due to their compact design. As they are thin, these cables are ideal for limited spaces and need continuous airflow to cool down.
Flat
Flat, ribbon-like Ethernet cables easily run under the baseboards, doors, and carpets. Moreover, these are preferable for such constructions as they lower the tripping problems and can be hidden easily.
Solid Core
Solid copper wires are best for longer and higher-quality installations than copper-wrapped aluminum. Since they provide strong, concrete signals to receivers, distortion and noise cannot affect the data.
Armored
Electricians prefer armored cables for outdoor and other harsh environments, where the cables are more likely to get abrasions. These cables provide extra protection due to thick jacketing and added layers.
Braided
Braided cables have nylon braiding over the conducting core that minimizes damage. Also, it makes the cable flexible so that you can run them around any nook and corner.
Gel Filled
Gel-filled cables are best outdoors where you need to prevent moisture from reaching the metal. Since these cables have an extra gel layer outside the cable to prevent water and other liquids from passing, it makes the cable moisture-resistant.

Caption: Ethernet attached to ports
Choosing the Right Ethernet Cable Type
To choose the right cable for your job, you must pick the one with suitable performance and range. For that, you can consider the following things.
- Look into the speed of your internet. For example, Cat6 will work best at typical speeds, and you can spend many years without changing it. However, Cat5e can also be a good choice while saving you some money.
- Remember that your choice of wire will not increase your internet speed; it will only carry the signals your provider sends.
- Test your internet speed via any speed testing software to confirm your speed. Moreover, it will help you in choosing the wire.
- Using a local network, consider the type of files you send and receive and choose accordingly. For example, you must send videos and high-quality graphics frequently for work purposes. In such cases, the higher the quality of Ethernet, the greater will be your work efficiency and vice versa. However, lower-quality cables can be a better choice to save a penny if your files are small enough.
- For replacement cables, try to go for an upgraded version from the one you already have. This will ensure better speeds and make your setup futureproof for many years. Thus, experts recommend the latest Cat6 and Cat6a cables as they can work with many high-end network devices.
Conclusion
Choosing an Ethernet cable can be tricky when so many choices are available. But, just a little research and in-depth study can enable you to start your journey without fear.
Over time, you will become an expert if you work in the same industry. For more information, visit our blog at Cloom.
