North American households have used polarized power cables and plugs as safety measures for years. Yet, not all homeowners know the difference between polarized cables.
Furthermore, they don’t know why the distinction exists. Some devices require polarized connectors to function correctly. But why?
Also, how can you tell the difference between polarized and non-polarized cables? The following guide will answer questions such as these and more.
Table of Contents
- Why Are Polarized Power Cables Necessary?
- AC Polarization
- How To Identify Polarized Power Cables
- Conclusion
Why Are Polarized Power Cables Necessary?
Most American households use power outlets with Type A and B sockets. This is according to guidelines set by the U.S. Department of Commerce.
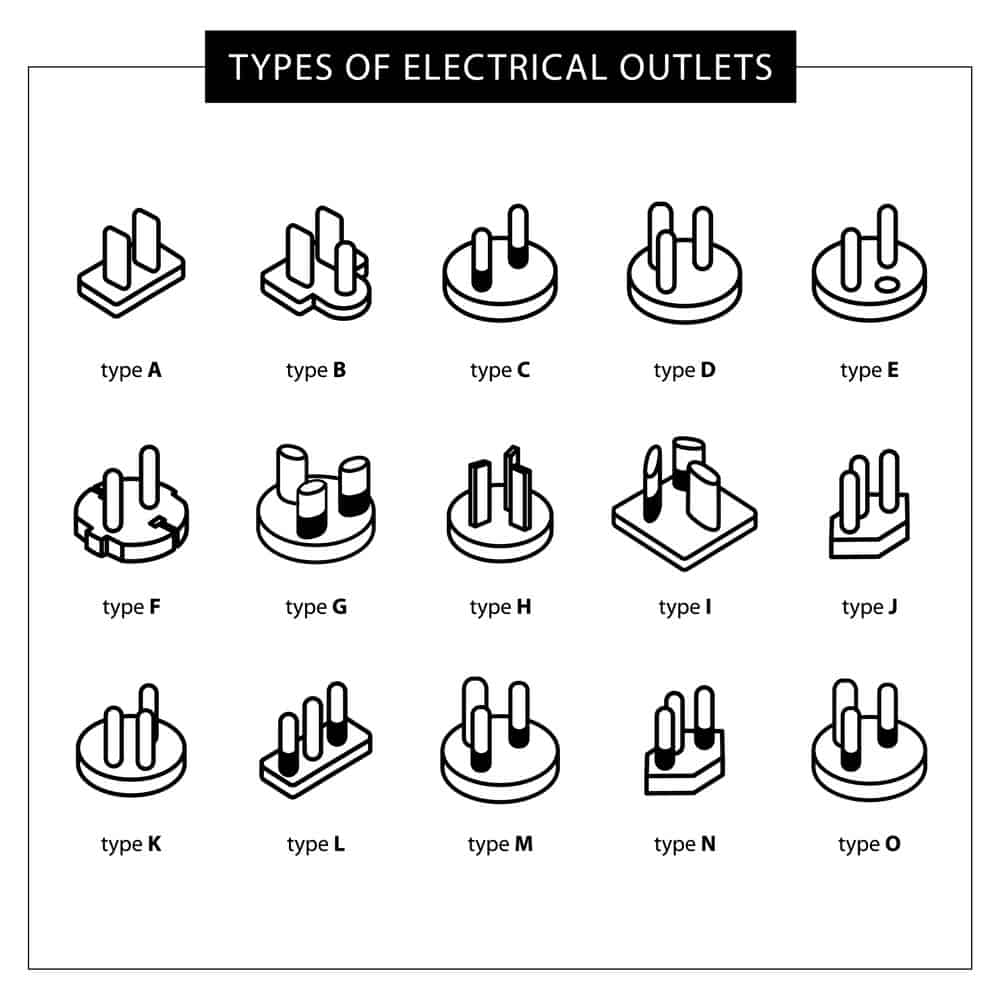
Types of Power Outlets
You may have noticed that most Type-A outlet sockets are not even in size. This is true for some connectors too.
However, finding plugs or connectors with identical poles/pins is also fairly common.
Most type-b power plugs have two identically sized neutral and live prongs. This is in addition to their ground prongs.
But why do all these variations exist? There is a special reason for this. It mostly concerns how electricity flows through your house and devices. It’s a process people refer to as AC Polarization.
AC Polarization
The term outlet may mislead you into believing that electricity streams one way out of your power sockets. This is not the case.
When you plug a device into an outlet, this creates a circuit. Thus, current flows through the live/hot side and back into the neutral. If you reverse the polarity, the neutral carries the current instead.
This can cause short circuits and other electrical hazards. The hot/live side of the circuit usually has a switch.
The connected device is always on when reversing the polarities because the neutral feeds the current.
How To Identify Polarized Power Cables
As this guide previously mentioned, you can identify a plug belonging to a polarized cable by the size of its prongs. If one prong is larger than the other, it is a polarized cable.
If both type-a prongs are the same size, then it is non-polarized.
Most non-polarized cables do not have integrated switches. However, you must note that plugs and prongs aren’t the only way to control a device’s current (polarize).
2-slot power cords with type-b or type-c prong configurations can also come in polarized varieties. Small household appliances and devices rely on these types of connectors and cables.
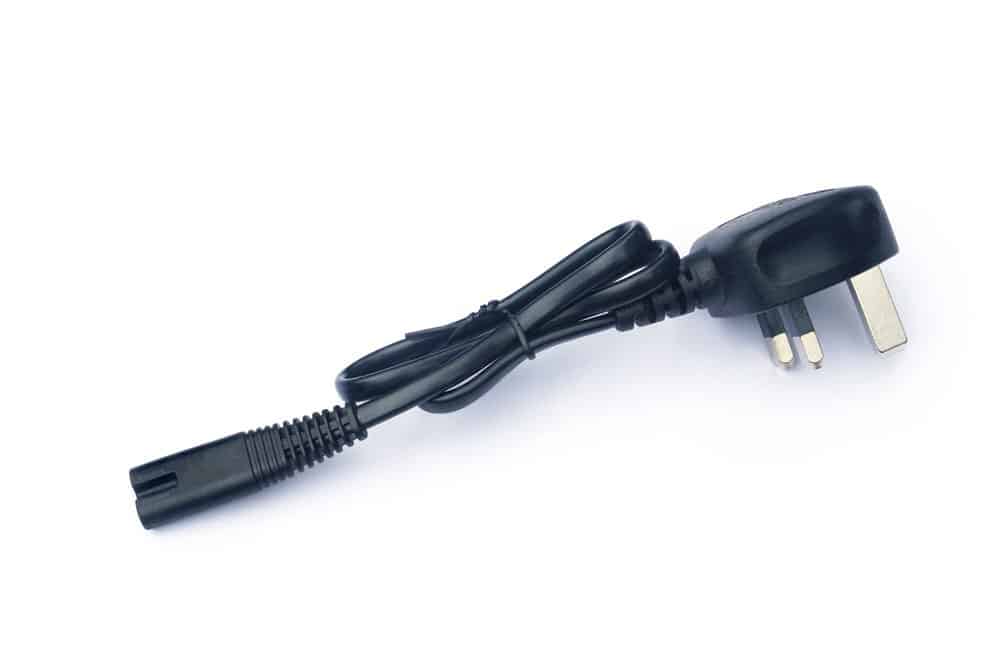

Type-b power cord
This includes CD players, DVD players, gaming consoles, laptops, and camera chargers. You can identify a polarized power cord by its figure-eight type connector.
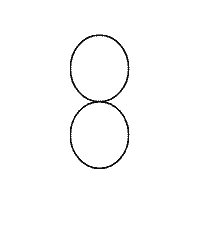
Figure eight
Non-polarized power cables and cords are similar to polarized cables in appearance. However, where the polarized cable has a figure-eight, its non-polarized counterpart consists of a semi-circle on top of a circle.
non-polarized connector
As such polarized and non-polarized cables are not compatible with each other. As this guide covered, the shape is not the only reason. Polarization dictates the current direction and flows for safety and functionality.
Conclusion
For your safety and the functionality of your devices, it’s important to choose your power cables carefully when shopping. You must understand the configuration of both your outlet and device.
In most cases, it’s better to play it safe and purchase the polarized option. Nevertheless, don’t hesitate to ask me any questions about the power cables.
